NEWS
What You Need To Know About M-pox
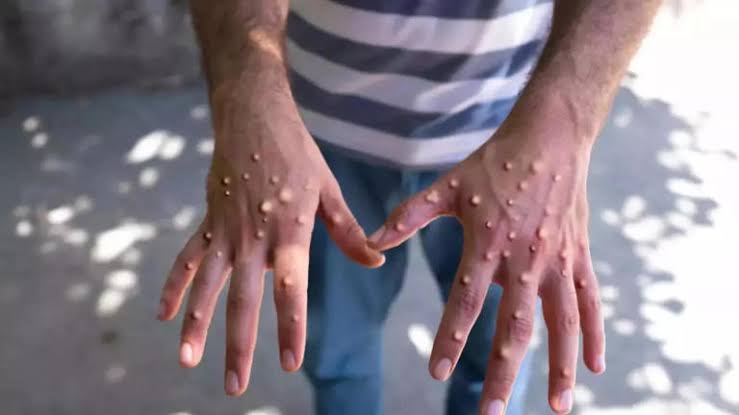

M-pox, also known as monkeypox, is a viral disease that has gained increased attention due to recent outbreaks in various parts of the world.
Though it was initially identified in monkeys, the disease can affect humans as well. Understanding M-Pox, its symptoms, transmission, and prevention is important in controlling its spread and protecting the public.
What Is M-pox?
M-pox is a viral infection caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox. However, M-Pox is generally less severe than smallpox.
The virus was first discovered in 1958 in research monkeys, which is how it got its name. The first human case was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Since then, M-pox has mostly been reported in Central and West African countries, but recent outbreaks have spread to other regions.
Symptoms of M-pox
The symptoms of M-Pox are similar to those of smallpox but are usually milder. They typically appear 5 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. Early symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
A few days after the onset of fever, a rash develops. The rash often starts on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body. The rash progresses through several stages, from flat lesions to raised bumps, then to fluid-filled blisters, and finally to scabs. The entire illness usually lasts 2 to 4 weeks. While M-Pox is generally not fatal, severe cases can occur, particularly in children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Transmission of M-pox
M-pox spreads through close contact with an infected person or animal. This can happen through direct contact with the rash, bodily fluids, or respiratory droplets. The virus can also spread by touching contaminated objects like bedding or clothing. Animal-to-human transmission can occur through bites or scratches from infected animals or by consuming undercooked meat from infected animals.
Human-to-human transmission is less common but can happen in close-contact situations, such as within households or during caregiving. The spread of M-Pox outside of Africa has raised concerns about the potential for wider outbreaks, especially in areas where the virus is not commonly found.
Preventing M-pox involves several key steps:
- Avoid Contact with Infected Animals: In regions where M-Pox is common, avoid contact with animals that could be infected, particularly rodents and primates.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after contact with animals or people who might be infected.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Healthcare workers and caregivers should use appropriate PPE when caring for someone with M-Pox.
- Isolate Infected Individuals: To prevent the spread, infected individuals should be isolated until they are no longer contagious.
There is no specific treatment for M-Pox, but the smallpox vaccine has been shown to provide some protection against the virus. Antiviral medications and supportive care can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. In areas with outbreaks, vaccination and public health measures are crucial in controlling the spread.
M-Pox, while similar to smallpox, is a distinct disease that poses its own set of challenges. Being aware of its symptoms, modes of transmission, and preventive measures is essential in managing the disease and preventing outbreaks.
Discover more from Asiwaju Media
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
-
 NEWS6 days ago
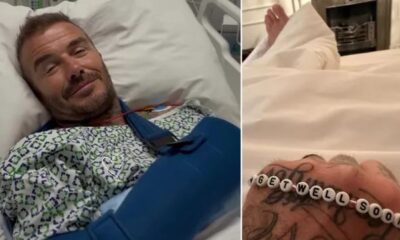
NEWS6 days agoDavid Beckham Hospitalized With Arm Injury As Victoria Shares Update
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 days ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 days agoFrank Edoho Confirms Split From Second Wife Sandra Onyenuchenuya
-

 NEWS5 days ago
NEWS5 days agoMan Heartbroken As Girlfriend Of 2 Years Denies Him During Interview With YouTuber Asherkine At UNN
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 days ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 days agoNollywood Mourns As Actor And Producer Kayode Peters Reportedly Passes Away In Canada
-

 JOBS/SCHOLARSHIPS6 days ago
JOBS/SCHOLARSHIPS6 days agoFG Releases YEIDEP 2025 Payment Schedule, Sparks Hope for Youth in Agribusiness
-

 INSIDE NYSC6 days ago
INSIDE NYSC6 days agoNYSC DG Calls For Unity and National Development During Lagos Camp Visit
-

 SPORTS6 days ago
SPORTS6 days agoAbakaliki FC Faces Kwara United Today in Federation Cup Final
-

 POLITICS4 days ago
POLITICS4 days agoChristian Asaga Nwali Bags Award for Contributions to Community Development
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 days ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 days agoUNN Student Becky Breaks Silence, Denies Claims Of Boyfriend Denial After Viral Outing With Asherkine
-

 NEWS6 days ago
NEWS6 days agoPhilanthropist Christian Asaga Nwali Commissions Bungalow for Elderly Widow in Ikwo
-

 POLITICS5 days ago
POLITICS5 days agoSenator George Akume Resigns as Secretary to the Government of the Federation
-

 SPORTS5 days ago
SPORTS5 days agoAfonja Warriors Spice Up the Final, Leave Rice Boys with an Empty Bowl